RanjanBhandari
Sunday, February 12, 2023
Saturday, December 11, 2010
Saturday, November 27, 2010
Ranjan's Photography...
Sunday, October 31, 2010
ಕನ್ನಡ ರಾಜ್ಯೋತ್ಸವದ ಹಾರ್ದಿಕ ಶುಭಾಶಯಗಳು !!.
 ಎಲ್ಲಾದರು ಇರು ಎಂತಾದರು ಇರು ||೨||
ಎಲ್ಲಾದರು ಇರು ಎಂತಾದರು ಇರು ||೨||ಎಂದೆಂದಿಗೂ ನೀ ಕನ್ನಡವಾಗಿರು
ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ಸತ್ಯ, ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ನಿತ್ಯ
ಕನ್ನಡ ಗೋವಿನ ಓ ಮುದ್ದಿನ ಕರು ||೨||
ಕನ್ನಡತನ ಒಂದಿದ್ದರೆ, ಅಮ್ಮಗೆ ಕಲ್ಪತರು
ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ಸತ್ಯ, ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ನಿತ್ಯ
ಎಲ್ಲಾದರು ಇರು ಎಂತಾದರು ಇರು
ಎಂದೆಂದಿಗೂ ನೀ ಕನ್ನಡವಾಗಿರು
ನೀ ಮೆಟ್ಟುವ ನೆಲ, ಅದೆ ಕರ್ನಾಟಕ
ನೀನೇರುವ ಮಲೆ ಸಹ್ಯಾದ್ರಿ
ನೀ ಮೆಟ್ಟುವ ನೆಲ, ಅದೆ ಕರ್ನಾಟಕ
ನೀನೇರುವ ಮಲೆ ಸಹ್ಯಾದ್ರಿ
ನೀ ಮುಟ್ಟುವ ಮರ ಶ್ರೀಗಂಧದ ಮರ ||೨||
ನೀ ಕುಡಿಯುವ ನೀರ್ ಕಾವೇರಿ
ಪಂಪನ ಓದುವ ನಿನ್ನಾ ನಾಲೆಗೆ
ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ಸತ್ಯ
ಕುಮಾರವ್ಯಾಸನ ಆಲಿಪ ಕಿವಿಯದು
ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ನಿತ್ಯ
ಎಲ್ಲಾದರು ಇರು ಎಂತಾದರು ಇರು
ಎಂದೆಂದಿಗೂ ನೀ ಕನ್ನಡವಾಗಿರು
ಹರಿಹರ ರಾಘವರಿಗೆ ಎರಗುವ ಮನ
ಹಾಳಾಗಿಹ ಹಂಪೆಗೆ ಕೊರಗುವ ಮನ
ಹರಿಹರ ರಾಘವರಿಗೆ ಎರಗುವ ಮನ
ಹಾಳಾಗಿಹ ಹಂಪೆಗೆ ಕೊರಗುವ ಮನ
ಬೆಳ್ಗೊಳ ಬೇಲೂರ್ಗಳ ನೆನೆಯುವ ಮನ
ಮಲೆನಾಡಿಗೆ ಹೊಂಪುಳಿ ಹೋಗುವ ಮನ
ಕಾಜಾಣಕೆ ಗಿಳಿ, ಕೋಗಿಲೆ ಇಂಪಿಗೆ
ಮಲ್ಲಿಗೆ ಸಂಪಿಗೆ ಕೇದಗೆ ಸೊಂಪಿಗೆ
ಕಾಜಾಣಕೆ ಗಿಳಿ, ಕೋಗಿಲೆ ಇಂಪಿಗೆ
ಮಲ್ಲಿಗೆ ಸಂಪಿಗೆ ಕೇದಗೆ ಸೊಂಪಿಗೆ
ಮಾವಿನ ಹೊಂಗೆಯ ತಳಿರಿನ ತಂಪಿಗೆ
ರೋಮಾಂಚನಗೊಳ್ಳುವ ಮನ
ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ಸತ್ಯ, ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ನಿತ್ಯ
ಎಲ್ಲಾದರು ಇರು ಎಂತಾದರು ಇರು
ಎಂದೆಂದಿಗು ನೀ ಕನ್ನಡವಾಗಿರು
ಎಲ್ಲಿದ್ದರೆ ಏನ್ ಎಂತಿದ್ದರೆ ಏನ್
ಎಲ್ಲಿದ್ದರೆ ಏನ್ ಎಂತಿದ್ದರೆ ಏನ್
ಎಂದೆಂದಿಗು ತಾನ್ ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ಸತ್ಯ ಕನ್ನಡವೇ ನಿತ್ಯ
ಅನ್ಯವೆನಲದೆ ಮಿಥ್ಯ
Wednesday, October 20, 2010
ALG - Application Level Gateway

An application-level gateway intercepts the incoming and outgoing packets, runs a proxy to copy and forward information across the gateway, and functions as a proxy server, thereby preventing any direct connection between a trusted server or client and an untrusted host.
Application-specific Proxies. Application-specific proxies accept only packets that are generated by services they are designed to copy, forward, and filter. There is a drawback here that is if a network relies only on an application-level gateway, incoming and outgoing packets cannot access services for which there is not a proxy. For example, if an application-level gateway runs a Telnet proxy, only packets generated by this service could pass through the firewall. All other services would be blocked.
Application-level Filtering. An application-level gateway runs proxies that examines and filters individual packets. This is achieved by checking each packet that passes through the gateway, verifying the contents of the packet up through the application layer of the OSI model. These proxies can filter particular kinds of commands or information in the application protocols the proxies are designed to copy, forward, and filter.
Saturday, July 24, 2010
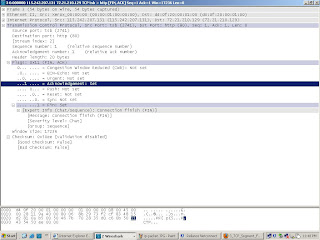
TCP Explained.
 Always on Time !!..The Transmission control protocol (TCP) Provides applications with reliable ,connection-oriented service and provides full logical path between two hosts on disparate networks .
Always on Time !!..The Transmission control protocol (TCP) Provides applications with reliable ,connection-oriented service and provides full logical path between two hosts on disparate networks .This article is an attempt to detail the different fields available in the TCP segment .
Source and Destination port :Its a 16 bit field that specifies the source and destination applications for the encapsulated data.
RFC 1700 describes all the ports number in common and not so-common use (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1700.txt).
A port number for an application ,which is combined with an ip address of the applications where host resides in , is called a socket .
Sequence number : Its a 32 bit identifier which identifies where the encapsulated data is fits within a data stream .
If the sequence number of a segment is 1 and the segments contains 512 octets ..the next segment should have sequence number of 1+512=513.
Acknowledgment number :Its a 32 bit field which tells what would be the sequence number the source expects to receive from destination.
If a hosts receives a acknowledgment number that doesn't match the next sequence number it intends to send , it concludes that packets earlier sent has not reach the destination and it will re-transmits the same.
Header Length :Its a data offset and a four bit field indicates the length of the header in 32-bit words and indicates the beginning of the data.
Reserved Field :Its of six bites ..which are always set to zero.
Flags :They are six 1-bit flags that used for data flow and control .
URG -Urgent
ACK-Acknowledgment
PSH-Push
RST-Reset
SYN-Synchronize
FIN-Final
Window Size: 16 bit field used for flow control .It specifies the number of octets,starting with the octet in indicated by acknowledgment number, that the sender of the segment will accept from its peer.
It specifies how much data it can handle or process at a time .
Checksum: Its a 16 bit field covering both the header and the encapsulated data,allowing error detection.
Urgent pointer :Its again a 16 bit field ..its used only when the URG Flag is set..urgent pointer added to the sequence number indicating the end of the urgent data.
Options :Optional field .One good example is maximum segment size ..which indicates what will be the maximum segment size sender is willing to accept .
The remainder of the field is padded with zeroes to ensure that the header length is multiple of 32 octets .
Here below is an example of TCP packet capture details using Wireshark